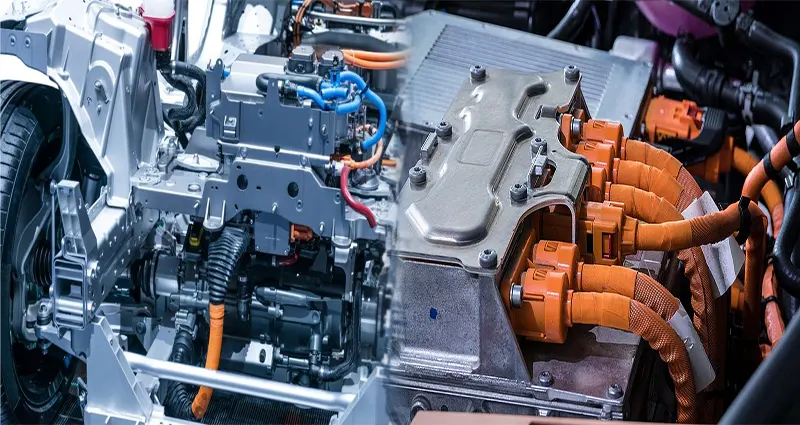
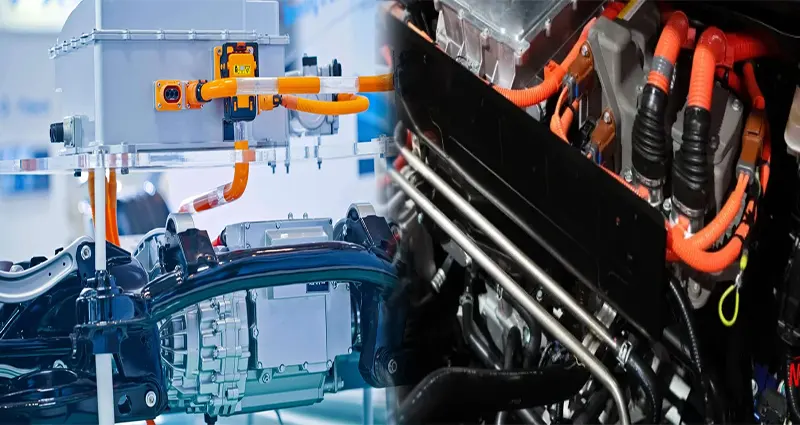
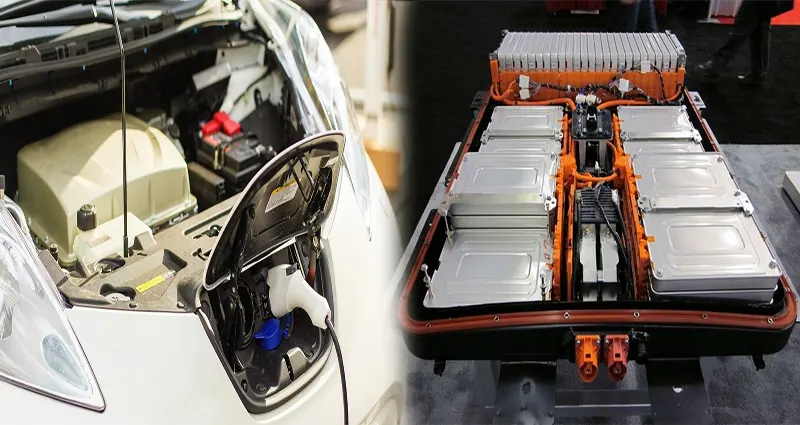
Types of Electric Car Charging Systems and Their Efficiency
As electric vehicles continue to gain popularity due to their environmental benefits and cost-effective operation, the demand for efficient and reliable charging systems is on the rise. Various types of electric car charging systems are available to cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding the different options can help electric vehicle owners optimize their charging experience. Here are some of the most common types of electric car charging systems and their efficiency:
Level 1 Charging
Level 1 charging is the most basic and slowest form of charging for electric vehicles. It involves using a standard 120-volt household electrical outlet to deliver power to the vehicle’s battery. While Level 1 charging is convenient and accessible, it is also the least efficient option as it provides the slowest charging speeds. This type of charging is ideal for overnight charging or for emergency situations when a faster charger is not available.