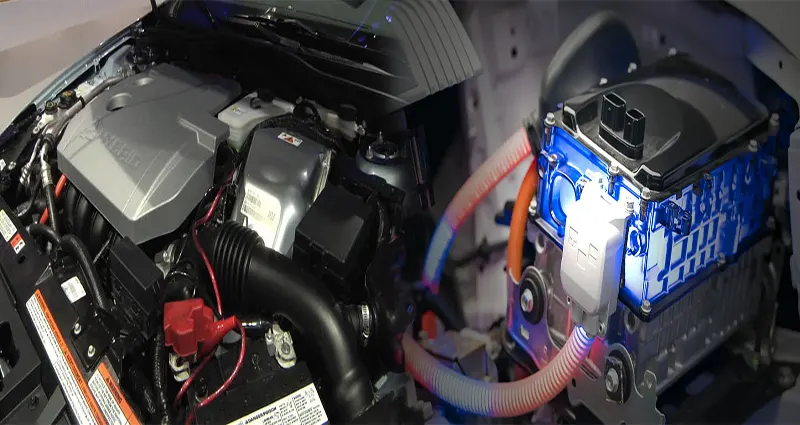
The automotive industry is undergoing a transformative shift towards sustainability, with electric vehicles (EVs) emerging as a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. Understanding the differences between traditional and electric car mechanics is crucial in appreciating the unique characteristics and technological advancements of these two types of vehicles.
Traditional Car Mechanics
Traditional cars, also known as internal combustion engine vehicles, have been the dominant mode of transportation for decades. These vehicles rely on an engine that burns fuel (gasoline or diesel) to generate power, which is then transmitted to the wheels through a complex system of components, including the transmission, pistons, and exhaust system.
Key Components of Traditional Cars:
- Internal Combustion Engine: The heart of a traditional car, the engine burns fuel to produce mechanical power.
- Transmission: The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for speed variation.
- Exhaust System: Responsible for removing harmful gases produced during combustion and reducing emissions.
- Fuel System: Distributes fuel from the tank to the engine for combustion.
Electric Car Mechanics
On the other hand, electric cars operate using an electric motor powered by a battery pack. This fundamental difference in propulsion technology results in a unique set of components and systems that distinguish electric vehicles from their traditional counterparts.
Key Components of Electric Cars:
- Electric Motor: Replaces the internal combustion engine, converting electrical energy into mechanical power.
- Battery Pack: Stores and supplies energy to power the electric motor.
- Inverter: Converts DC power from the battery into AC power for the electric motor.
- Regenerative Braking System: Recaptures energy during braking and deceleration to recharge the battery.
Differences in Performance and Maintenance
- Acceleration: Electric cars typically offer instant torque delivery, providing quick acceleration and responsive performance compared to traditional cars, which may experience lag due to the combustion process.
- Maintenance: Electric cars have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance than traditional cars, which have complex engine components and systems that need regular servicing.
- Efficiency: Electric cars are more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, as they do not produce tailpipe emissions and can be powered by renewable energy sources.
Future Outlook
As electric vehicles continue to gain traction in the marketplace, advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and performance capabilities are driving the evolution of electric car mechanics. The shift towards electrification represents a significant step towards reducing carbon emissions, improving air quality, and promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
Understanding the differences between traditional and electric car mechanics sheds light on the technological innovations reshaping the automotive industry. While traditional cars have long been synonymous with mobility, electric vehicles offer a cleaner and more efficient alternative that is shaping the future of transportation. By recognizing the unique features and operational principles of each vehicle type, consumers can make informed choices that align with their preferences and values in the era of sustainable mobility.